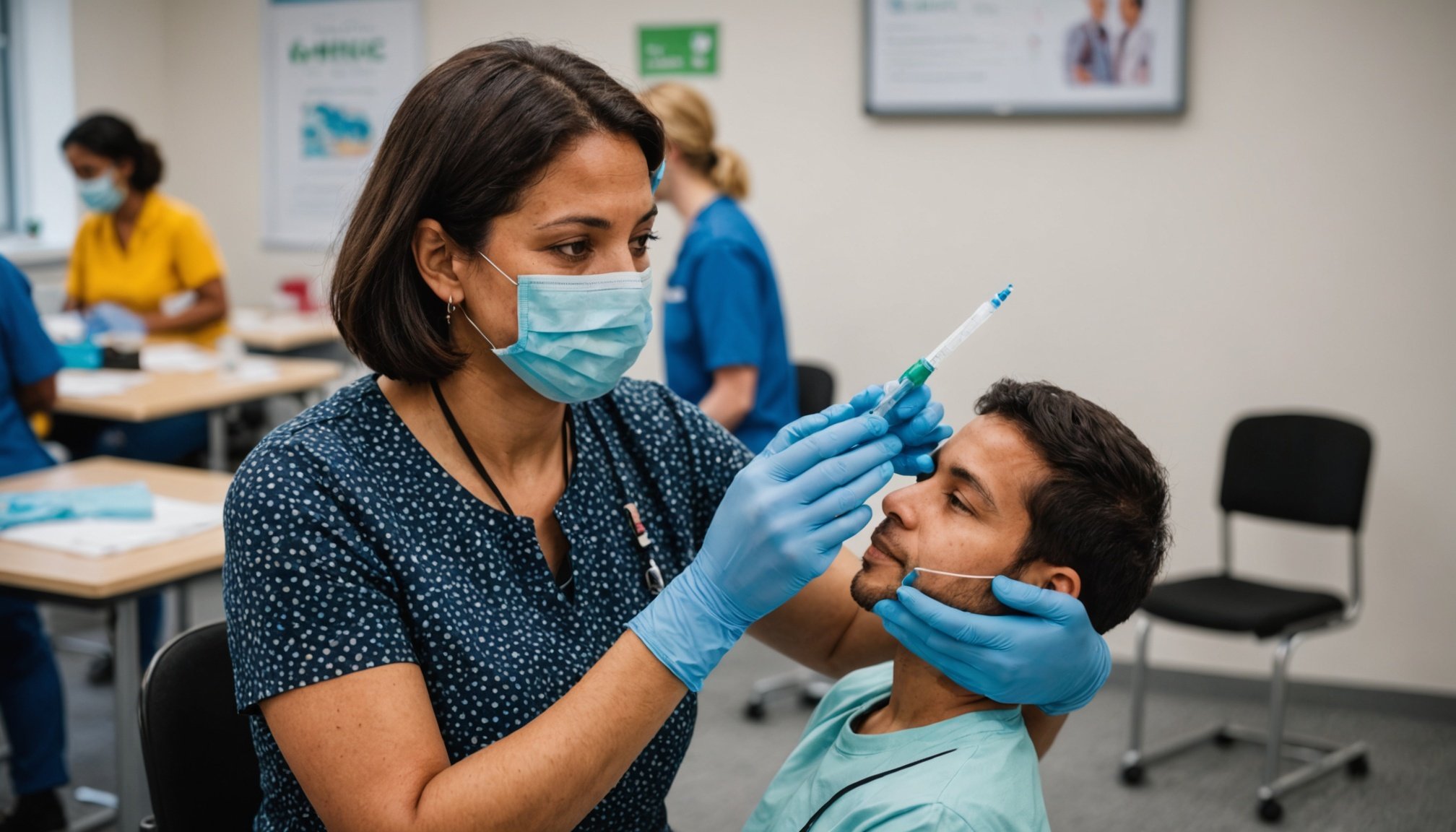
As the world continues to adapt to the ongoing challenges posed by COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, health professionals in the UK play a critical role in the vaccination efforts. With diverse populations across the country, it is essential for healthcare providers to understand the latest guidelines for administering vaccines effectively. This article explores the current recommendations provided by the NHS and other relevant authorities, focusing on how to ensure that all individuals receive the necessary immunisation services they need. We will delve into the unique considerations for various population groups, the importance of equity in healthcare, and how to mitigate risks associated with low vaccination rates. Let’s examine these guidelines closely.
Understanding the Importance of Vaccination in Diverse Populations
Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health, safeguarding not only the individuals who receive the dose but also the wider community. In the UK, the NHS has prioritized vaccination as a pivotal strategy in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, particularly in the context of COVID-19 and its variants like SARS-CoV. The latest guidelines emphasize that health professionals must adapt their approaches to cater to the diverse backgrounds of the people they serve.
In the same genre : Exploring Cutting-Edge Strategies by UK Allergists for Managing Adult-Onset Asthma
In recent years, disparities in vaccination uptake have been observed among different communities. These disparities often align with socio-economic factors, cultural beliefs, and access to healthcare services. For instance, certain ethnic groups may have lower vaccination rates due to historical mistrust of medical systems or cultural practices that discourage immunisation. Thus, understanding these nuances is crucial for health professionals aiming to improve vaccination rates among children and adults alike.
The NHS guidelines encourage healthcare providers to actively engage with patients from diverse backgrounds. This can involve outreach programs that educate communities about the benefits of vaccination. Tailoring communication strategies to resonate with specific groups can enhance trust and encourage more people to get vaccinated. Moreover, health professionals are urged to consider language barriers and provide information in multiple languages to ensure comprehensibility and accessibility of vaccination information. By fostering an inclusive environment, health professionals can significantly reduce the risks associated with low vaccination rates and contribute to the overall goal of herd immunity.
In parallel : How can UK health professionals improve communication with patients who have language barriers?
Current Guidelines for Vaccine Administration by Health Professionals
As of December 2024, the NHS has outlined comprehensive guidelines for health professionals regarding the administration of vaccines in diverse populations. These guidelines serve as a framework to ensure effective and equitable immunisation practices across the UK.
One of the key aspects of the current guidelines is the emphasis on informed consent. Healthcare providers must ensure that individuals understand the benefits and potential risks associated with vaccination. This includes discussing the specific vaccines available, such as those for COVID-19, the flu, and other preventable diseases. By being transparent about the administration process, health professionals can help alleviate fears and promote a more positive attitude towards vaccination.
Additionally, the guidelines stress the importance of maintaining accurate records of vaccinations. This not only assists in tracking individual immunisation statuses but also helps public health officials monitor vaccination coverage across different demographics. Such data is vital for identifying communities with lower vaccination uptake and designing targeted interventions to improve access and education.
Health professionals are also encouraged to be culturally competent. This means understanding the specific health beliefs and practices of different populations. For example, some individuals may have dietary restrictions or may be hesitant about certain vaccines due to religious beliefs. Tailoring vaccination programs to account for these factors can significantly enhance participation rates. Moreover, the guidelines advise healthcare providers to ensure that all vaccination sites are accessible to everyone, including those with disabilities, ensuring that no one is left behind in the vaccination effort.
Enhancing Access to Vaccination Services
Access to vaccination services is a significant barrier for many communities. The latest NHS guidelines address this issue by outlining strategies to enhance accessibility for all populations, particularly marginalized groups.
One approach recommended by the guidelines is the establishment of mobile vaccination clinics. These clinics can travel to underserved areas, providing essential immunisation services to those who may have difficulty reaching healthcare facilities. By bringing the services directly to the communities, health professionals can significantly increase vaccination rates among children and adults.
Moreover, community partnerships play a crucial role in enhancing access. Collaborating with local organizations, schools, and religious institutions can facilitate outreach efforts and provide trusted voices within communities. These partnerships can organize educational workshops that explain the benefits of vaccines and address common misconceptions that may exist.
The guidelines also highlight the importance of flexible scheduling. Providing evening and weekend appointments can accommodate those who work standard hours and may find it challenging to visit healthcare facilities during regular hours. This flexibility can directly contribute to higher vaccination uptake, particularly among working families and individuals with multiple commitments.
Additionally, the guidelines advocate for public awareness campaigns that promote the importance of vaccination. These campaigns should utilize various media channels, including social media, radio, and community bulletin boards, to disseminate accurate information about available vaccines and their benefits. By raising awareness and directly addressing the concerns of different populations, health professionals can foster a culture of vaccination, ultimately reducing the health risks posed by preventable diseases.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy Among Individuals
Vaccine hesitancy has emerged as a significant challenge in the administration of immunisations, particularly for COVID-19 vaccines. The latest guidelines from the NHS recognize the importance of addressing hesitancy effectively to increase vaccination rates among various populations.
Health professionals are encouraged to engage in open dialogues with patients. This involves listening to their concerns and providing evidence-based information to dispel myths surrounding vaccination. Addressing misinformation is critical in building trust and encouraging more individuals to get vaccinated.
The guidelines suggest utilizing peer educators—individuals who share similar backgrounds or experiences with the target population. These educators can effectively convey the importance of vaccination in a relatable manner, thereby increasing the likelihood of acceptance. Additionally, health professionals are advised to share personal experiences of vaccination, emphasizing the benefits not only for individual health but also for community well-being.
Moreover, the guidelines highlight the importance of empathy and understanding in these conversations. Many individuals may have legitimate fears based on personal experiences or cultural narratives. By acknowledging these feelings and providing a supportive environment, health professionals can facilitate a more positive dialogue about vaccination.
Lastly, the guidelines emphasize the role of follow-up communications. Sending reminders about upcoming vaccinations or providing updates on vaccine developments can keep the conversation alive and encourage individuals to follow through with their immunisation plans. Such proactive measures can help ensure that more people become and remain vaccinated, thereby contributing to the broader public health goals of the UK.
The latest NHS guidelines for administering vaccines in diverse populations underscore the importance of inclusivity, accessibility, and effective communication in the vaccination process. By adhering to these guidelines, health professionals can play a pivotal role in improving vaccination rates among all individuals, regardless of their backgrounds.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of public health, it is crucial to recognize that each community has unique needs and concerns. By fostering trust and understanding, healthcare providers can overcome barriers that prevent people from seeking immunisation services. In doing so, we can work together towards a healthier future where the risks associated with preventable diseases are significantly reduced for everyone. The time to act is now, and every effort counts in the quest for comprehensive health and well-being in the UK.